The prode.com site has been updated, goto main page to continue the navigation !
Frequently Asked Questions
What Prode thermoPhysical Properties generator does ?
This tool provides a thermodynamic framework for calculating thermophysical properties (equilibrium, transport etc.) of pure components and multicomponent's streams. Entirely written in C++ language (and part of a set of classes for thermodynamic calc's) it is available in form of DLL for direct access from electronic sheets, user-defined programs etc.
What a library is ?
A dynamic-link library (DLL) is a binary file that acts as a shared library of functions that can be used simultaneously by multiple applications. A DLL integrates with spreadsheets (Microsoft EXCEL, LOTUS 1-2-3 etc.) , user defined programs (Visual-Basic, C, C++ etc.) providing additional methods (functions) , extending features etc. Being a compiled code it runs very fast so providing an effective mean to extend application's features.
How do I include this tool in software I am distributing ?
There is a developer licence for this, ask Prode for details.
What data and structures does this framework include ?
Prode Physical Properties generator (base version) includes a compilation with physical properties data on 970+ components and a set of procedures for calculating properties of pure and multicomponent streams.
How many components does a stream include ?
A stream entity may include from 1 (pure) up to 500 comp's , the user can define the max number, a stream with a large number of components requires a somewhat large time to solve.
How do I define the thermodynamic models ?
Each stream has its own thermodynamic model for equilibrium, enthalpy, entropy calc's, this allows a great flexibility being the model directly associated to the stream composition.
How do I define 20 or more streams (to simulate a complex plant) ?
Prode allows to define 100 or more different streams. A large number of streams is frequently required for simulating complex plants, Prode thermoPhysical Property generator has built-in functions to manage all requirements (computer memory allocation , stream's definition and access etc.)
How do I reference a stream ?
Stream are referenced by a numeric code (a integer) in calling functions, a typical call is : setop(stream, double t, double p), where the value of stream (integer 1-100) references the stream.
How do I define a stream (and access data) ?
Prode distribution includes a few graphical objects, under windows there is a editor from where to access all stream's data (gas & liquid flow, component's percentages, thermodynamic models etc.). This is useful for defining stream's compositions and have a immediate view of stream's data. In addition several methods permit to read and set all stream's properties.
How do I enter Binary Interaction Parameters (BIP's) ?
In stream's definition form a table permits to enter Binary Interaction Parametres. All non-ideal thermodynamic methods (EOS and Activity Coefficents) may require the definition of these parameters to work as intended. BIP's are available in literature (DECHEMA etc. sources), another way is to regress equilibrium data supplied by the user.
How do I define stream's operating conditions ?
There is a specific method for defining a new operating condition : setop(stream, double t, double p), which requires a stream, operating pressure and temperature, this method performs an isothermal flash and sets operating conditions.
How do I perform isothermal, isoenthalpic, isentropic, liquid-fraction flash operations ?
Several different flash operations are supported : T-P, T-V, T-H, T-PF, H-P, S-P, V-P....
License agreement
Agreement made between Prode "Prode" and "User".
- Prode is the owner of the product "Prode Properties" including , but not limited to, dynamic link libraries, static libraries, header files, sample programs, utility programs, together with the accompanying documentation collectively known as the "software"
- User desires to obtain the right to utilize the software, the parties hereby agree as follows Personal license A version with limited features is available for personal use at home or in educational establishments for teaching purposes, all other applications, without first obtaining a commercial license from Prode, are expressly prohibited. Commercial license Upon full payment of the license fee the User has full right to utilize the purchased number of units of the software, a unit is defined as one copy of the software or any portion thereof installed on one stand-alone computer, for networked computers one unit shall be applied for each user having concurrent access and one unit shall be applied for the server.
- Prode grants the nonexclusive, nontransferable right to use the software.
- User has a royalty free right to reproduce and distribute the software as available from Prode Internet server (personal licence) provided that User doesn't remove or alter any part of the software or of the licensing codes and threat the software as a whole unit.
- You cannot decompile, disassemble or reverse engineer the files containing the licensed software, or any backup copy, in whole or in part.
- You cannot rent, lease or sublicense the Licensed Software without express agreement by Prode.
- The software is provided *as is, where is* , Prode does not warrant that software is free from defects, or that any technical or support services provided by Prode will correct any defects which might exist.
- Prode shall not be liable for any damages that may result directly or indirectly from the use of these software programs including any loss of profits, loss of revenues, loss of data, or any incidental or consequential damages that may arise out of use of these software.
- Your license is effective upon your acceptance of this agreement and installing the Licensed Software.
- This license agreement shall remain in effect until the Licensed Software will be in use.
- You may terminate it at any time by destroying the Licensed Software together with all copies. It will also terminate if you fail to comply with any term or condition of this Agreement.
- You agree upon such termination to destroy all copies of the Licensed Software in any form in your possession or under your control.
Excel application example : calculate properties of pure fluids and mixtures
With Prode Properties it is easy to calculate the properties of a pure fluid or a mixture,this Excel application example shows how to calculate a value in a cell and print table of values for different properties in a specified range of temperature and pressure
First step: define the stream (components, compositions etc.)
Properties includes a Stream editor which permits to access all informations (as compositions, operating conditions, models, options) for all streams which you need to define, to access the Stream editor from Excel Properties menu select Edit Properties
The Stream editor includes several pages, from the first page you can select a stream (Properties can store all the streams required to define a medium size plant) solve a series of flash operations and see the resulting compositions in the different phases, in this page select the stream you wish to define, for example the first.
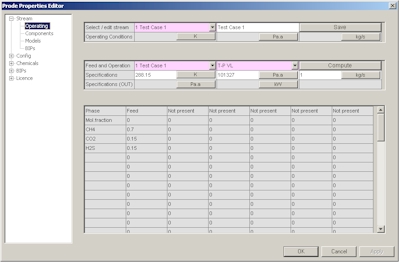
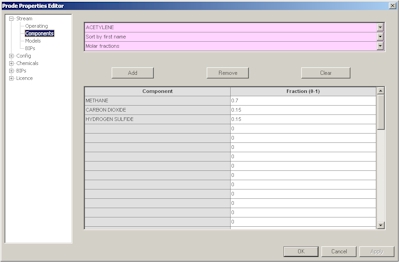
In the second page you can define a new composition or modify an existing composition, in this example we define C1 0.7 CO2 0.15 H2S 0.15 as molar fractions
In the third page you can define the package (thermodynamic models and related options) , here we define API Soave Redlick Kwong.
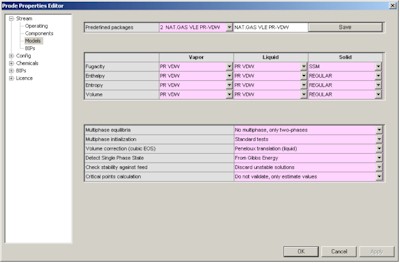
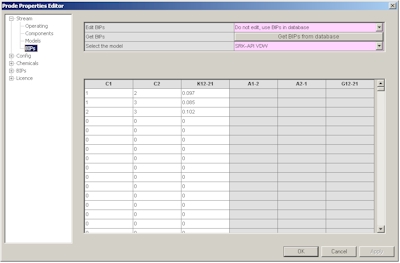
The fourth page provides access to BIP (Binary Interaction Parameters) for the different models, you can enter specific values or click on "Load BIPs" button to get the predefined BIPs from databank.
Finally we must save the new data, in the first page click on "Save" button, note that you can redefine the name of the stream as you wish (editing the cell near the button "Save"), you can define / modify many streams following the procedure described.
Once defined the stream you may wish to define the units which we wish to utilize in our problem, in stream editor go then to the "Units" dialog
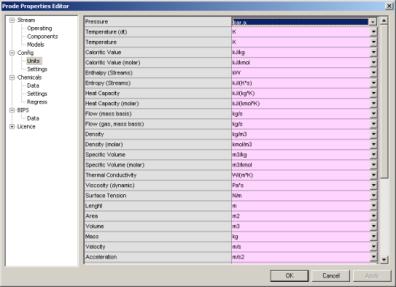
here you can select the units which you need for a specific problem, in this example for the pressure (first row) select Bar.a , notice that unit for temperature is K (but you can set the units which you prefer) then click on Ok button to accept new values and leave the Properties editor.
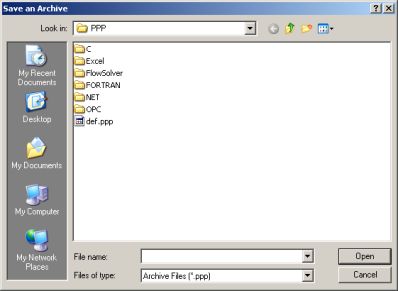
Now you are ready to use Properties for calculating all the properties which you need, however there is still a last thing to do if you do not wish to lose all data when leaving a Excel page, precisely to save data to a file, to save data to a file from Excel Properties menu select "Save a Archive"

then select the file "def.ppp" if you wish that Properties utilizes this data as default (this is the normal , recommended option), differently set a different name (you can for example define different names for different projects) but you will need to load that specific Archive before to make calcs for that project and since Excel reloads Properties with any new page this may result tedious...
Properties saves on the file also the units of measurement so you can define different streams and different units in different projects.
Now you can calculate all the properties which you need with the units which you prefer for all the streams defined in that project.
Second step: calculate properties in Excel cells.
Suppose we wish to calculate the densities for the mixture defined in stream 1 directly in the cells, in B3 we enter the macro =EStrLD(1,B1,B2) , for calculating liquid density of stream 1 at temperature specified in B1 and pressure specified in B2 ,in B4 we enter the macro =EStrGD(1,B1,B2) for calculating the gas density and in B5 the macro =EStrLf(1,B1,B2) for calculating the liquid fraction
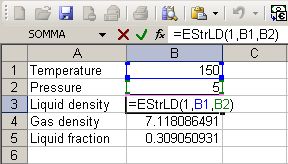
In B1 we enter 200 as temperature (remember we have K as unit) and in B2 we enter 5 as pressure (remember we have set Bar.a as unit), densities are in Kg/m3 , notice that when you change B1 or B2 Prode Properties recalculates these values. Now you can modify the stream 1 (changing the list of components, the compositions or models) or the units of measurement and Prode Properties will calculate the value of densities and liquid fraction accordingly, in this way is very easy with Excel to solve many different problems leaving to Prode Properties the task to calculate all properties for pure fluids and mixtures.
Calculate properties in Matlab.
From Matlab command line you can call the methods in Prode Properties by typing the names, for example to calculate cp/cv at specified conditions
>> EstrGCp(1,300,500000)/EstrGCv(1,300,500000)
>> ans = 1.3211
or, to calculate the speed of sound for vapor phase at same conditions
>> EstrGSS(1,300,500000)
>> ans = 374.1625
in Matlab (as In Excel) you can access the Properties editor from menu associated with the figure.

Herebelow a short list of the properties available, read the operating manual for additional information.
- Phase fraction (vapor, liquid, solid)
- (True) critical point pressure of mixtures
- (True) critical point temperature of mixtures
- Cricondentherm temperature of mixtures
- Cricondentherm pressure of mixtures
- CricondenBar temperature of mixtures
- CricondenBar pressure of mixtures
- Cloud point temperature of mixtures
- Cloud point pressure of mixtures
- Flash point of flammable mixtures
- Enthalpy of gas / vapor phase
- Enthalpy of liquid phase
- Enthalpy of solid phase
- Entropy of gas / vapor phase
- Entropy of liquid phase
- Entropy of solid phase
- Density of gas / vapor phase
- Density of liquid phase
- Density of solid phase
- Isobaric specific heat (Cp) of gas / vapor phase
- Isobaric specific heat (Cp) of liquid phase
- Isochoric specific heat (Cv) of gas / vapor phase
- Isochoric specific heat (Cv) of liquid phase
- Gas heating value
- Gas Specific gravity
- Joule Thomson coefficients of gas / vapor phase
- Joule Thomson coefficients of liquid phase
- Isothermal compressibility of gas / vapor phase
- Isothermal compressibility of liquid phase
- Volumetric expansivity of gas / vapor phase
- Volumetric expansivity of liquid phase
- Speed of sound in gas / vapor phase
- Speed of sound in liquid phase
- Speed of sound in gas+liquid (mixed) phase
- Viscosity of gas / vapor phase
- Viscosity of liquid phase
- Thermal conductivity of gas / vapor phase
- Thermal conductivity of liquid phase
- liquid Surface tension
Third step: calculate tables of values and print graphs.
Finally we will see how to calculate and graph tables of values in a range of temperatures for many different properties (liquid fraction, cp, cv, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, speed of sound) for both gas and liquid phases, for doing this we will use a predefined Excel page, from Excel menu File->open , in Excel folder (in Prode Properties installation) select the file props.xls
If you wish you can modify the stream composition or the units of measurement , in that case, as before from Properties menu access the Properties editor and modify the previous data. Then enter (in the proper units) the desired range of temperatures (cells B2-B3) and the operating pressure (cell B4) and click on compute button to calculate the data, Prode Properties will print the values with the desired units of measuremebt.
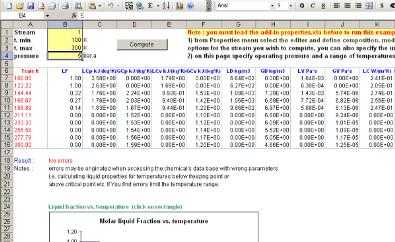
In the same page there are a series of graphs which show the different properties at different operating conditions.
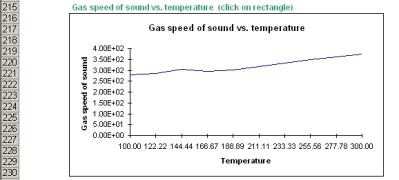
As you see Properties is a useful tool in everyday work, you can calculate rigorously, easily and quickly many different properties, you can set preferred units, you can define and save many different streams.
Technical features overview (Windows version)
- Entirely written in C++ (since first edition, 1993)
- Up to 100 different streams with up to 50 components per stream (user can redefine)
- Several compilations of chemical data and BIPs are available, the user can add new components and BIPs
- Proprietary compilation with data for more than 1600 chemicals and 30000 BIPs
- flexible database format (support for up to 30 different correlations) works with all majour standards including DIPPR.
- Comprehensive set of thermodynamic models, base version includes
- Regular
- Wilson
- NRTL
- UNIQUAC
- UNIFAC
- Soave-Redlich-Kwong (standard and extended version with parameters calculated for best fitting of vapor pressure, density and enthalpy)
- Peng-Robinson (standard and extended version with parameters calculated for best fitting of vapor pressure, density and enthalpy)
- Benedict Webb Rubin (Starling) BWRS
- Steam Tables IAPWS 95
- ISO 18453 (GERG 2004)
- ISO 20765 (AGA 8 model)
- Lee-Kesler (Plocker) LKP
- CPA Cubic Plus Association (SRK and PR variants)
- Hydrates (Cubic Plus Association, Van Der Waals-Platteeuw)
- additional models as Pitzer, NRTL for electrolyte solutions, PC SAFT (with association), GERG (2008) etc.
- van der Waals and complex mixing rules to combine equations of state with activity models
- Huron Vidal
- Wong Sandler ( WS )
- Michelsen ( MHV2 )
- Tassios et al. ( LCVM )
- Base and Extended EOS versions with parameters calculated to fit experimental data from DIPPR and DDB
- Selectable units of measurement
- Procedure for solving fluid flow including multi phase equilibria and heat transfer
- Procedure for solving staged columns
- Rigorous solution of distillation columns, fractionations, absorbers, strippers...
- Procedure for calculating hydrate formation temperature and hydrate formation pressure
- hydrate phase equilibria based on different Van Der Waals-Platteeuw models
- Procedure for solving polytropic compression with phase equilibria
- Huntington method for gas phase
- Proprietary method for solving a polytropic process with phase equilibria
- Procedure for solving isentropic nozzle (safety, relief valve with single and two phase flow)
- HEM, Homogeneous Equilibrium
- HNE-DS, Homogeneous Non-equilibrium
- NHNE, Non-homogeneous Non-equilibrium
- Procedure for simulating fluid flow in piping (pipelines) with heat transfer
- Beggs and Brill and proprietary methods for single phase and multiphase fluid flow with heat transfer
- Procedure for fitting BIP to measured VLE / LLE / SLE data points (data regression)
- Procedure for fitting BIP to VLE values calculated with UNIFAC
- Functions for simulating operating blocks (mixer, gas separator, liquid separator) **
- Functions for accessing component data in database (the user can define mixing rules)
- gas / vapor-liquid-solid fugacity plus derivatives vs. temperature pressure composition
- gas / vapor-liquid-solid enthalpy plus derivatives vs. temperature pressure composition
- gas / vapor-liquid-solid entropy plus derivatives vs. temperature pressure composition
- gas / vapor-liquid-solid molar volume plus derivatives vs. temperature pressure composition
- Flash at Bubble and Dew point specifications and P (or T)
- Flash at given temperature (T) and pressure (P) multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, isothermal flash
- Flash at given phase fraction and P (or T), solves up to 5 different points
- Flash at given enthalpy (H) and P multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes adiabatic flash
- Flash at given enthalpy (H) and T multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes adiabatic flash
- Flash at given entropy (S) and P multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes isentropic flash
- Flash at given entropy (S) and T multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes isentropic flash
- Flash at given volume (V) and P multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes isochoric flash
- Flash at given volume (V) and T multiphase vapor-liquid-solid, includes isochoric flash
- Flash at given volume (V) and enthalpy (H) multiphase vapor-liquid-solid
- Flash at given volume (V) and entropy (S) multiphase vapor-liquid-solid
- Flash at given enthalpy (H) and entropy (S) multiphase vapor-liquid-solid
- Rigorous (True) critical point plus Cricondentherm and Cricondenbar
- Complete set of properties for different states
- gas density
- vapor density
- liquid density
- solid density
- gas Isobaric specific heat (Cp)
- vapor Isobaric specific heat (Cp)
- liquid Isobaric specific heat (Cp)
- gas Isochoric specific heat (Cv)
- vapor Isochoric specific heat (Cv)
- liquid Isochoric specific heat (Cv)
- gas cp/cv
- liquid cp/cv
- Gas heating value
- Gas Wobbe index
- Gas Specific gravity
- gas Joule Thomson coefficients
- vapor Joule Thomson coefficients
- liquid Joule Thomson coefficients
- gas Isothermal compressibility
- vapor Isothermal compressibility
- liquid Isothermal compressibility
- gas Volumetric expansivity
- vapor Volumetric expansivity
- liquid Volumetric expansivity
- gas Speed of sound
- vapor Speed of sound
- liquid Speed of sound
- vapor + liquid (HEM) Speed of sound
- gas Viscosity
- vapor Viscosity
- liquid Viscosity
- gas Thermal conductivity
- vapor Thermal conductivity
- liquid Thermal conductivity
- gas compressibility factor
- vapor compressibility factor
- liquid Surface tension
Typical applications
- Fluid properties in Excel, Matlab, Mathcad and other Windows and UNIX (**) applications
- Thermodynamics, physical, thermophysical properties
- Process simulation
- Heat / Material Balance
- Process Control
- Process Optimization
- Equipments Design
- Separations
- Instruments Design
- Realtime applications
- petroleum refining, natural gas, hydrocarbon, chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, air conditioning, energy, mechanical industry